
In the earlier blogs we discussed about the Stages of Design Thinking, how to use Empathy to connect Empathy Research and then how to Define the problem statements. In this blog, we will discuss how to ideate. Before this step we were not thinking of solution. Now is the time to deep dive solutions for identified & prioitrised problems.
Brainstorm Solutions
Here the goal is to plan sessions to gather a diverse group of team members, including designers, travel coordinators, HR representatives, and even employees who frequently travel. In these sessions, participants can freely share their ideas. Following points need to be considered for the brainstorming sessions:
- Encourage Wild Ideas: Encourage participants to think outside the box and propose even the most unconventional or wild ideas. This can help spark creative thinking and lead to innovative solutions.
- Use Design Thinking Techniques: Employ techniques like “How Might We” questions to reframe challenges as opportunities. For example:
- “How might we make the booking process as simple as ordering a meal?”
- “How might we ensure seamless communication across time zones?”
- Combine and Build on Ideas: Encourage participants to build on each other’s ideas. Encourage collaboration and the merging of concepts to create more comprehensive solutions.
- Sketch and Visualize: Have participants sketch out their ideas visually. These rough sketches can help convey concepts and make them more tangible.
- Explore Digital Tools: Utilise digital collaboration tools that allow remote team members to contribute their ideas in real-time. Tools like virtual whiteboards can facilitate visualizing ideas collectively.
- Divergent Thinking: Encourage participants to think broadly and consider a wide range of possibilities. Avoid narrowing down too quickly; the goal is to generate a large pool of potential solutions.
- Quantity Over Quality: Quantity is important at this stage. Aim to generate a multitude of ideas without getting hung up on evaluating their feasibility at this point.
- Idea Cards or Sticky Notes: Write down each idea on separate cards or sticky notes. This makes it easy to physically move and group ideas for further exploration.
- Iterate and Refine: Encourage participants to iterate on their ideas. They can take an idea they’ve generated and refine it, add details, or take it in a different direction.
- Combine and Cluster: Group similar or related ideas together. This can lead to the emergence of themes or concepts that can be explored further.
- Select Promising Ideas: Review the generated ideas and identify the most promising ones that align with the defined problem statements and criteria.
Eisenhower Matrix
Named after U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower, this prioritisation framework will help you organise your tasks and activities by importance and urgency. The ideas generated in the brainstorming session can be plotted in this matrix to understand the prioirities.
For our problem of business travel experience for BlogTree.in employees, an example of the matrix can be something as below. The 2nd quadrant (HIGH Importance & HIGH Urgency) lists the items which are the ideas which should be focussed first. Other quadrants can be taken further based on future requirements.
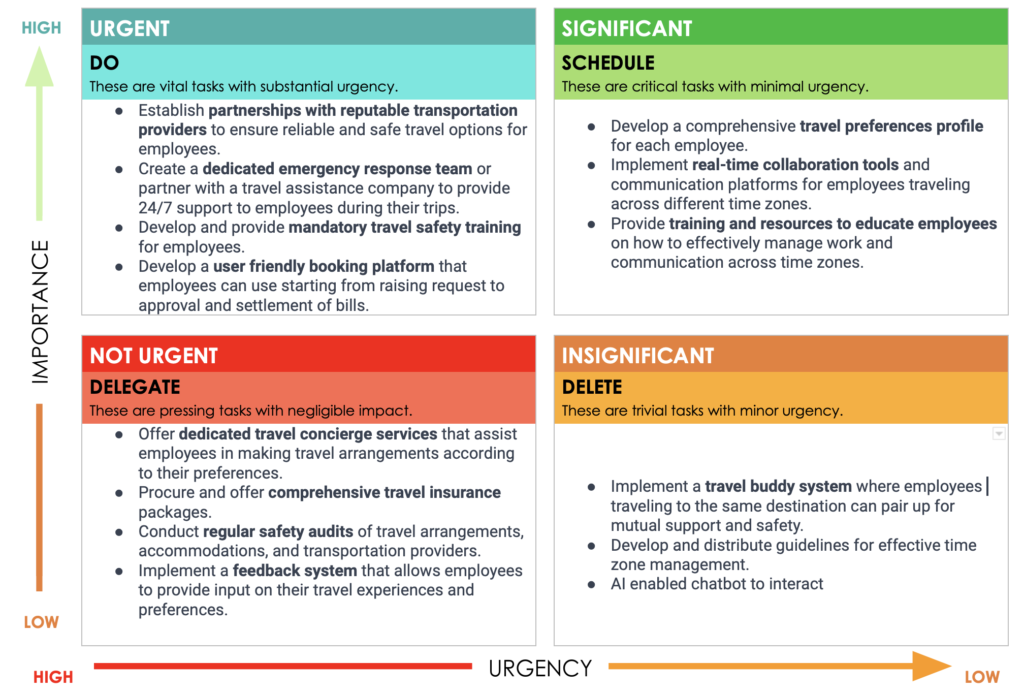
By the end of the “Ideate” stage, you’ll have a diverse collection of creative ideas that can serve as a foundation for further development. These ideas will guide the process of prototyping and testing potential solutions to create a travel experience that addresses the needs of BlogTree.in’s employees.
During the ideation phase, teams generate a wide range of ideas and possibilities. It encourages participants to think freely, suspend judgment, and explore unconventional solutions. Brainstorming sessions, mind maps, and other creative techniques are commonly employed to stimulate innovative thinking.
After the Ideate stage comes the Prototype & Test stage. Lets dive deep into them.
